概述
在mybatis中动态sql是一项非常重要的功能,它是灵活构建sql的基石,现在我们就来看看mybatis是如何实现动态sql这一功能的。
写个简单的测试用例用于debug。
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="com.learn.mybatis.bean.Employee">
select id, last_name lastName, email, gender
from employee
<where>
<if test="lastName != null">
last_name = #{last_name} and
</if>
<if test="email != null">
email = #{email} and
</if>
</where>
</select>
初始化
mybatis在解析到 select、insert、update、delete等节点时,会将这些节点分别创建 XMLScriptBuilder 对象进行解析创建出 SqlSource 对象。
public XMLScriptBuilder(Configuration configuration, XNode context, Class<?> parameterType) {
super(configuration);
// context 则为sql语句的根节点,如 <select XXX>XXXX</select>
// PS:已经 include 中的数据替换掉 include 节点,(在XMLIncludeTransformer该类中处理)
this.context = context;
this.parameterType = parameterType;
// 预先设置好 节点处理器
initNodeHandlerMap();
}
调用 parseScriptNode 就会解析xml节点数据,创建 SqlSource 对象。
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource;
// 在sql节点内部需要有 ${} 或者 其他的子节点存在才会生成 DynamicSqlSource ,否则也不需要使用动态sql的功能。
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
protected MixedSqlNode parseDynamicTags(XNode node) {
List<SqlNode> contents = new ArrayList<>();
NodeList children = node.getNode().getChildNodes();
// 遍历xml节点内部的各种数据。
for (int i = 0; i < children.getLength(); i++) {
XNode child = node.newXNode(children.item(i));
if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE || child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.TEXT_NODE) {
// 如果是 文本节点数据则创建 TextSqlNode
String data = child.getStringBody("");
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(data);
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
// 判断文本中是否有 ${}
contents.add(textSqlNode);
isDynamic = true;
} else {
contents.add(new StaticTextSqlNode(data));
}
} else if (child.getNode().getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) { // issue #628
// 如果是 节点,如 <where>、<if>等
String nodeName = child.getNode().getNodeName();
// 预先设置好的 节点处理器 进行解析数据
NodeHandler handler = nodeHandlerMap.get(nodeName);
if (handler == null) {
throw new BuilderException("Unknown element <" + nodeName + "> in SQL statement.");
}
handler.handleNode(child, contents);
isDynamic = true;
}
}
return new MixedSqlNode(contents);
}
private void initNodeHandlerMap() {
nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("when", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("otherwise", new OtherwiseHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("bind", new BindHandler());
}
来看看 节点处理器的 结构
private interface NodeHandler {
void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents);
}
private class WhereHandler implements NodeHandler {
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
// 采用递归的形式创建该节点下的数据
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
WhereSqlNode where = new WhereSqlNode(configuration, mixedSqlNode);
targetContents.add(where);
}
}
private class IfHandler implements NodeHandler {
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
// 采用递归的形式创建该节点下的数据
MixedSqlNode mixedSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(nodeToHandle);
// 获取 表达式
String test = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("test");
IfSqlNode ifSqlNode = new IfSqlNode(mixedSqlNode, test);
targetContents.add(ifSqlNode);
}
}
private class BindHandler implements NodeHandler {
@Override
public void handleNode(XNode nodeToHandle, List<SqlNode> targetContents) {
// 获取 name 和value 属性
final String name = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("name");
final String expression = nodeToHandle.getStringAttribute("value");
final VarDeclSqlNode node = new VarDeclSqlNode(name, expression);
targetContents.add(node);
}
}
在解析完毕之后的rootSqlNode,如图所示。
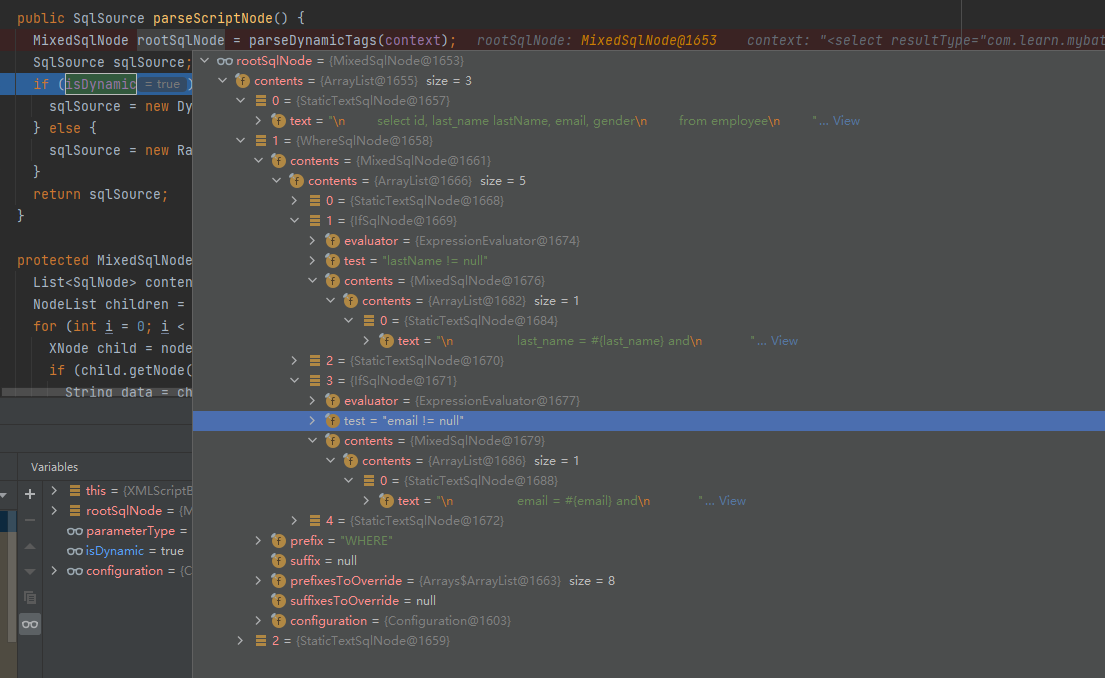
SqlNode的信息在下面进行说明。
运行时构建
在上面的初始化过程中根据xml节点数据创建出了 一些SqlNode对象,而这些SqlNode对象就是动态Sql的关键了,下面我们来看看mybatis是如果通过 SqlNode 创建出sql语句的。
想来看看 SqlNode 接口 及 实现关系
public interface SqlNode {
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
在 DynamicSqlSource#getBoundSql 方法中
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
//... 其他操作
return boundSql;
}
在DynamicContext类中,通过sqlBuilder存储逐步解析出来的sql语句片段
private final StringJoiner sqlBuilder = new StringJoiner(" ");
public void appendSql(String sql) {
sqlBuilder.add(sql);
}
public String getSql() {
return sqlBuilder.toString().trim();
}
MixedSqlNode
// 构造器中创建,组合模式
private final List<SqlNode> contents;
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
contents.forEach(node -> node.apply(context));
return true;
}
StaticTextSqlNode
private final String text; // 构造器中创建
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
context.appendSql(text); // 直接将文本内容 放置在sql中
return true;
}
TextSqlNode
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 用于替换 ${} 占位符数据
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter));
context.appendSql(parser.parse(text));
return true;
}
VarDeclSqlNode
private final String name; //<bind>节点 name
private final String expression; //<bind>节点 value
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 从参数中的个别属性设置别名。
final Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(expression, context.getBindings());
// DefaultParameterHandler#setParameters 方法中会被用到
context.bind(name, value);
return true;
}
WhereSqlNode
private static List<String> prefixList = Arrays.asList("AND ","OR ","AND\n", "OR\n", "AND\r", "OR\r", "AND\t", "OR\t");
public WhereSqlNode(Configuration configuration, SqlNode contents) {
super(configuration, contents, "WHERE", prefixList, null, null);
}
TrimSqlNode
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
//先将trim节点下的sql片段暂存在
FilteredDynamicContext filteredDynamicContext = new FilteredDynamicContext(context);
boolean result = contents.apply(filteredDynamicContext);
filteredDynamicContext.applyAll();
return result;
}
// FilteredDynamicContext 为 FilteredDynamicContext 内部类
private class FilteredDynamicContext extends DynamicContext {
private DynamicContext delegate;
private boolean prefixApplied;
private boolean suffixApplied;
private StringBuilder sqlBuffer;
public void applyAll() {
sqlBuffer = new StringBuilder(sqlBuffer.toString().trim());
String trimmedUppercaseSql = sqlBuffer.toString().toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.length() > 0) {
applyPrefix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
applySuffix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
}
delegate.appendSql(sqlBuffer.toString());
}
@Override
public void appendSql(String sql) {
sqlBuffer.append(sql);
}
@Override
public String getSql() {
return delegate.getSql();
}
private void applyPrefix(StringBuilder sql, String trimmedUppercaseSql) {
if (!prefixApplied) {
prefixApplied = true;
if (prefixesToOverride != null) {
for (String toRemove : prefixesToOverride) {
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.startsWith(toRemove)) {
sql.delete(0, toRemove.trim().length());
break;
}
}
}
// 添加前缀 prefix 在 TrimSqlNode 对象中
if (prefix != null) {
sql.insert(0, " ");
sql.insert(0, prefix);
}
}
}
private void applySuffix(StringBuilder sql, String trimmedUppercaseSql) {
if (!suffixApplied) {
suffixApplied = true;
if (suffixesToOverride != null) {
for (String toRemove : suffixesToOverride) {
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.endsWith(toRemove) || trimmedUppercaseSql.endsWith(toRemove.trim())) {
int start = sql.length() - toRemove.trim().length();
int end = sql.length();
sql.delete(start, end);
break;
}
}
}
// 添加后缀 suffix 在 TrimSqlNode 对象中
if (suffix != null) {
sql.append(" ");
sql.append(suffix);
}
}
}
}
ForEachSqlNode
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
Map<String, Object> bindings = context.getBindings();
// 获取foreach中的迭代数据
final Iterable<?> iterable = evaluator.evaluateIterable(collectionExpression, bindings, Optional.ofNullable(nullable).orElseGet(configuration::isNullableOnForEach));
if (iterable == null || !iterable.iterator().hasNext()) {
return true;
}
boolean first = true;
// 在sql中添加 open 属性
applyOpen(context);
int i = 0;
for (Object o : iterable) {
DynamicContext oldContext = context;
if (first || separator == null) {
context = new PrefixedContext(context, "");
} else {
// 在sql中 设置每次迭代之间的分隔符
context = new PrefixedContext(context, separator);
}
int uniqueNumber = context.getUniqueNumber();
// 在 bind 中设置 index 和 item 临时变量数据, 和全局数据(__frch_ + index/item名词 + 序号)
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map.Entry<Object, Object> mapEntry = (Map.Entry<Object, Object>) o;
applyIndex(context, mapEntry.getKey(), uniqueNumber);
applyItem(context, mapEntry.getValue(), uniqueNumber);
} else {
applyIndex(context, i, uniqueNumber);
applyItem(context, o, uniqueNumber);
}
// 将 sql语句中的 #{} 变量名词更改为全局的名词 (__frch_ + index/item名词 + 序号)
contents.apply(new FilteredDynamicContext(configuration, context, index, item, uniqueNumber));
if (first) {
// 第一次设置的 separator 为 空字符 ""
first = !((PrefixedContext) context).isPrefixApplied();
}
context = oldContext;
i++;
}
applyClose(context);
context.getBindings().remove(item);
context.getBindings().remove(index);
return true;
}
在 ExpressionEvaluator#evaluateIterable 方法中
public Iterable<?> evaluateIterable(String expression, Object parameterObject, boolean nullable) {
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(expression, parameterObject);
if (value == null) {
if (nullable) {
return null;
} else {
throw new BuilderException("XXXXX");
}
}
if (value instanceof Iterable) {
return (Iterable<?>) value;
}
// 如果是数组则转成Iterable
if (value.getClass().isArray()) {
int size = Array.getLength(value);
List<Object> answer = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Object o = Array.get(value, i);
answer.add(o);
}
return answer;
}
if (value instanceof Map) {
return ((Map) value).entrySet();
}
throw new BuilderException("XXXX");
}